4.1 amino acids are small organic molecules containing an amine and a carbonyl group
An amino acid is a small, organic molecule consisting of an amine group, a carboxylic acid and a side chain specific to each individual amino acid. The structure of an amino acid is shown below.
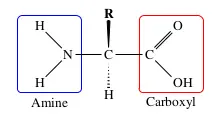
There are twenty naturally occurring (L) amino acids that generally make up the primary structure of a protein. These vary in structure by the side chain R. The exact nature of side chain R—structure,
Amino acids are zwitterions, with a positive charge on the amine group and a negative charge on the carbonyl group
deeper: protein primary structure for how amino acids join together
see: 4.1a A zwitterion contains both a positive and a negative charge for more on zwitterions
see: amino acid categories for how amino acids are generally classified